Definition
Adsorption
Adsorption is a physical process, also called physisorption. Pollutants (liquid, gas or suspended solids) will be adsorbed on the surface or pores of adsorbent materials. Adsorption is a reversible process without chemical reaction.
Absorption
Absorption refers to the process that pollutants penetrate into the structure of another substance, which is different from adsorption. Adsorption is that one substance exists on the surface of another substance.

Chemisorption
Chemical adsorption is related to physical adsorption process. Chemical adsorption refers to the adsorption generated by the chemical interaction between adsorbent and pollutants. Chemical adsorption is generally considered to be an irreversible process.
Catalysis
Catalysis is a process that changes the chemistry of another substance under the action of a catalyst. This change (usually causing or accelerating chemical reactions) will remove pollutants without any change in the catalyst itself.
Activated Carbon Physisorption
Activated Carbon Adsorption Principle
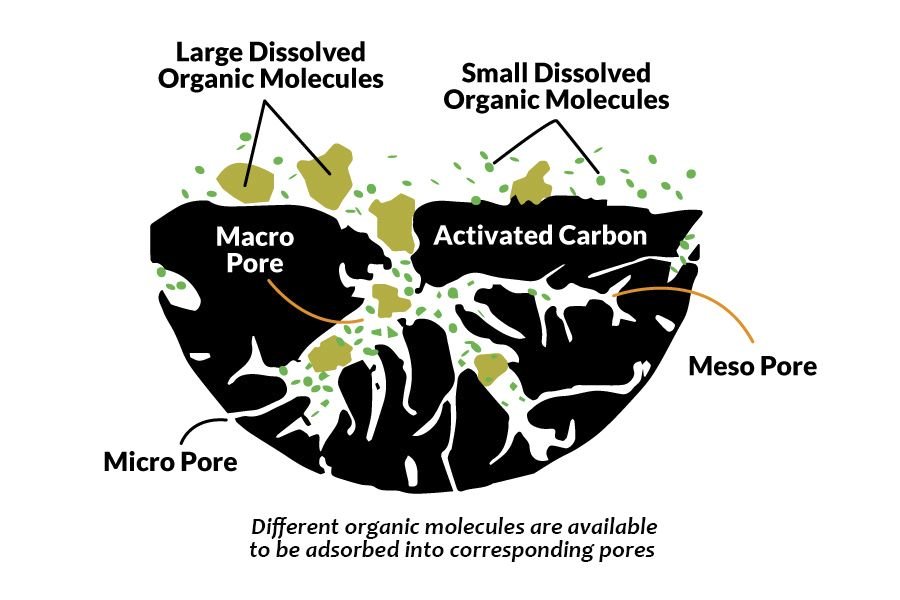
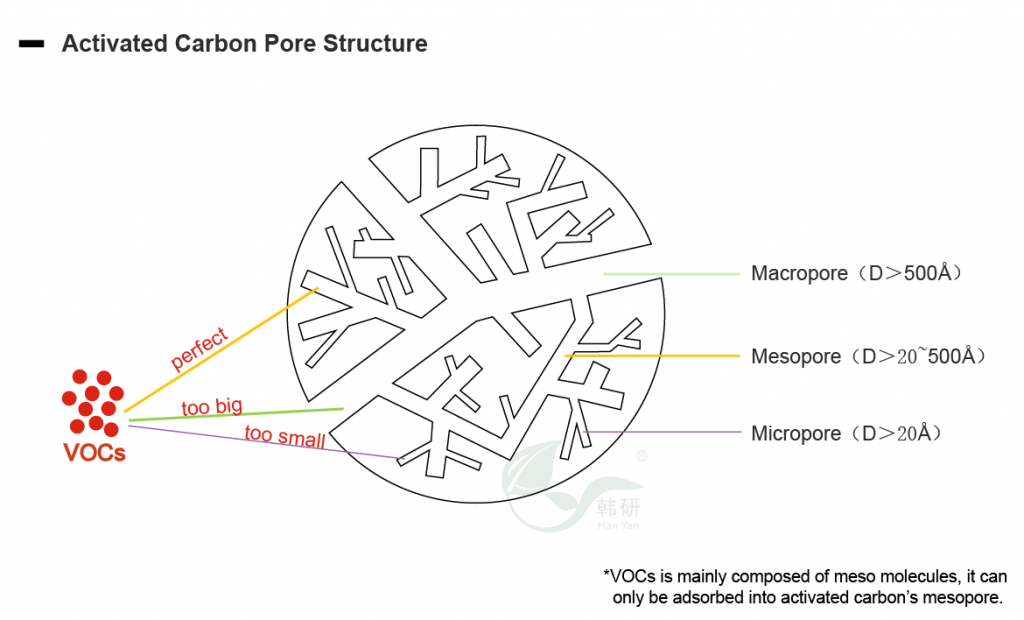
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is a form of carbon processed to have small, low-volume pores that increase the surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions(cr. Wikipedia). Activated carbon has developed pore structure, and based on Van der Waals Forces, these pores of activated carbon has adsorption forces to adsorb different impurities, and the adsorption performance is due to the polarity of them.
Activated Carbon Desorption
Because adsorption is a reversible process, high temperature desorption and regeneration can be carried out after activated carbon is completely saturated.
Activated Carbon Desorption Methods
High temperature desorption/Pressure drop desorption/Displacement desorption/ Purge desorption.
In practical application, several desorption methods are often combined for better performance. For example, steam desorption has the functions of heating and purging at the same time. 100℃ steam is generally suggested for desorption.
Activated Carbon Desorption Tips
The desorption temperature of volatile organic compounds is not related to its boiling point, but closely related to the saturated vapor pressure. Therefore, the appropriate desorption agent can be selected according to the saturated vapor pressure of the material to determine the appropriate desorption temperature.
Activated Carbon Chemisorption
Chemisorption is an irreversible process, certain impregnated activated carbon can optimize the highest performances for spcial pollutants removal. After the adsorption of activated carbon in this process is saturated, it needs to be collected by qualified recycling company for follow-up treatment according to hazardous waste solids.
Conclusion
Activated carbon purification is not an absorption process but adsorption.