Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Gel Slurry Sublimation?
- The Risks and Challenges of Sublimation
- How Activated Carbon Works
- Mechanisms of Preventing Sublimation
- Industrial Applications and Case Uses
- Advantages of Using Activated Carbon
- Best Practices for Implementation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Gel slurries are vital in adhesives, coatings, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. However, sublimation of volatile compounds within these formulations can compromise product quality and functionality. Activated carbon offers an efficient, scalable solution to this issue.
What Is Gel Slurry Sublimation?
Sublimation is the transition of a substance from solid or gel directly into vapor. In gels, this leads to the evaporation of active or volatile components, causing deterioration, volume loss, or destabilization of the slurry.
The Risks and Challenges of Sublimation
- Loss of active ingredients
- Product shrinkage or deformation
- Reduced adhesive or functional performance
- Shortened shelf life
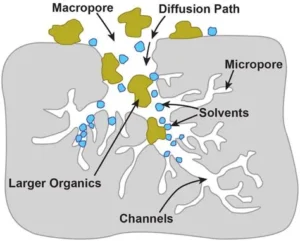
How Activated Carbon Works
Activated carbon has a microporous structure capable of adsorbing moisture, vapors, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This minimizes the free concentration of such elements around gels, reducing sublimation risk.
Mechanisms of Preventing Sublimation
Surface Adsorption of Volatile Compounds
Activated carbon captures VOCs and harmful gases, preventing them from leaving the gel matrix and causing sublimation.
Moisture Regulation and Humidity Control
By maintaining optimal humidity levels, activated carbon preserves the gel’s integrity and prevents drying-induced sublimation.
Chemical Stabilization
Certain carbon types can be impregnated with additives to chemically bind reactive vapors, increasing stability in sensitive applications.
Industrial Applications and Case Uses
- Electronic pastes and conductive gels
- Adhesive and sealant storage
- Pharmaceutical transdermal gel systems
- Coatings in high-humidity environments
Advantages of Using Activated Carbon
- High surface area for adsorption
- Safe and non-reactive
- Cost-effective and reusable
- Improves product shelf life and quality
Best Practices for Implementation
- Use sachets or containers near gel packaging
- Select activated carbon grade based on volatility of gel components
- Ensure regular replacement to maintain efficacy
Conclusion
Activated carbon plays a critical role in modern gel preservation. By mitigating sublimation through multiple mechanisms, it enhances the longevity and performance of industrial products, making it indispensable for many sectors.
FAQs
Q1: Can activated carbon be used in pharmaceutical gel packaging?
A1: Yes, with proper food or pharma-grade certification.
Q2: How long does it remain effective?
A2: Typically 3–6 months, depending on environment and application.
Q3: Will it affect the chemical formulation of my product?
A3: No, it works through physical adsorption, not chemical reaction.
Article Keywords: Activated Carbon Gel Sublimation, Preventing Gel Sublimation, Anti-Sublimation Activated Carbon, Gel Slurry Stabilization, Volatile Compound Adsorption, Adhesive Stability Solutions, Industrial Gel Applications, Eco-Friendly Activated Carbon, Pharmaceutical Gel Preservation, Moisture Control in Gel Systems